July 24, 2024
Share
More than 500 peer-reviewed publications have highlighted a range of applications of Arima Genomics’ technology, from evolutionary biology to genomic research. This week, we were pleased to see the British Journal of Haematology publish a clinical account of the real-world impact of our technology in identifying a cancer-driving gene rearrangement.
This story highlights the journey many clinicians face when genomic diagnostic tools based on linear sequencing methods fail to identify the molecular drivers of cancers and other diseases. We applaud the efforts of clinical researchers whose pioneering work using Hi-C technology offers a vision for a future where 3D genomics illuminates a path forward for more patients.
Perplexing Cancer Case Requires Innovative Diagnostic Solution
A 6-year-old boy was brought to a clinic to address persistent snoring and tonsillar hypertrophy. The initial solution seemed straightforward: a tonsillectomy. However, the procedure revealed cancerous cells in the boy’s tonsils, which presented signs of Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LBL) with IRF4 rearrangements (LBL-IRF4).
Despite the morphological and immunohistochemical evidence for LBL-IRF4, standard diagnostic tests including Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) at NeoGenomics and Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) at Foundation Medicine both returned negative results for the IRF4 rearrangement.
Arima Technology Identifies Key Variant Missed By Other Diagnostic Tools
Under a research protocol the team turned to Arima to explore the use of Hi-C technology for detecting structural variants and rearrangements. By preserving the three-dimensional conformation of the genome, the team aimed to determine if it could overcome the limitations of FISH and traditional NGS methods to identify the suspected IRF4 rearrangement.
Using Arima Hi-C reagents and protocols, our team successfully identified an IRF4 rearrangement, validating the suspected diagnosis of LBL-IRF4 and affirming the corresponding treatment plan for IRF4-driven lymphomas. The patient responded to the treatment and eventually achieved complete remission (Figure 1).
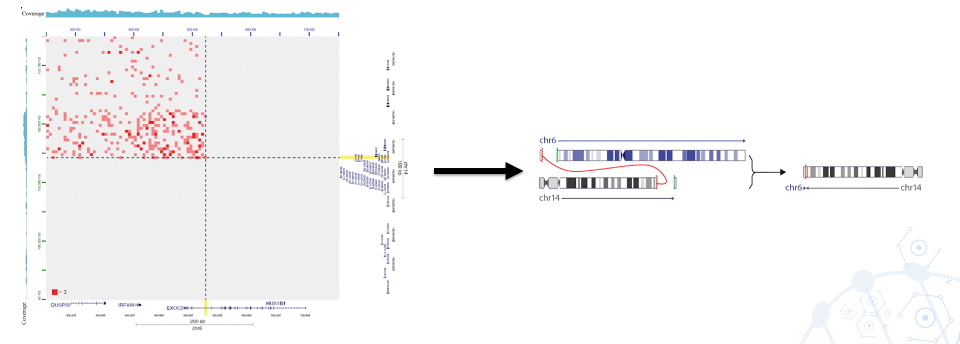
Figure 1: Arima-HiC+ chemistry yields 3D genome data that enables detection of an elusive Large B-Cell Lymphoma IRF4 rearrangement.
Translating Research Into Clinical Testing
From kits, RUO services, and CLIA-certified services through Aventa Genomics, Arima supports translational oncology research from discovery to application.
Arima Genomics is committed to pushing the boundaries of genomics from the bench to the clinic. Our focus remains on developing high quality tools which can be used across an expanding menu of applications to address a wider range of research questions and diagnostic challenges. Furthermore, Arima has established Aventa Genomics (www.aventagenomics.com), a subsidiary of Arima, which now offers the Aventa FusionPlus test at its CLIA-certified laboratory in Orlando, FL.
This case is a testament to the power of Arima Genomics’ Hi-C technology and the profound impact that innovative diagnostic tools can have on patient care. By providing accurate and timely diagnoses, these advanced technologies enable clinicians to develop more effective treatment plans, ultimately offering hope to patients and their families.
Learn more about this case in the British Journal of Haematology .
References:
- Chisholm KM, et al. IRF4 translocation status in pediatric follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019.
- Salaverria I, et al. Translocations activating IRF4 identify a subtype of germinal center-derived B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011.
- Arima Genomics Hi-C Technology. Arima Genomics.
- Xu J, et al. Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukemia. Nature. 2022.
- Mallard C, et al. Hi-C as a tool for precise detection and characterization of chromosomal rearrangements. Genome Biol. 2017.
- Ramis-Zaldivar JE, et al. Distinct molecular profile of IRF4-rearranged large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2020.
- Dixon JR, et al. Integrative detection and analysis of structural variation in cancer genomes. Nat Genet. 2018.
- Nikolic A, et al. Hi-C detects genomic structural variants in peripheral blood of pediatric leukemia patients. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2022.



