February 27, 2023
Share
Tuesday, February 28, is Rare Disease Day – a time to pause and help raise awareness about the 300 million people worldwide living with a rare disease, their families, and caregivers.

At Arima Genomics, we are passionate about helping scientists and clinicians better understand human health and disease through the power of 3D genomics. Recently, our Arima technology has been used to help better understand the mechanisms of several rare diseases, including ependymoma, glioma, leukemias, Ewing Sarcoma, and beta thalassemia.
So today, we would like to highlight and celebrate the work of some of these intrepid scientists and clinicians striving to improve the lives of those affected by rare diseases.
Using 3D Genomics to Understand Rare Disease Mechanisms and Identify Novel Therapeutic Targets
Ependymoma
Ependymoma is a rare tumor type, occurring more often in children than adults. Ependymoma is a form of glioma that arises in ependymal cells in the brain or spinal cord. The causes of ependymoma vary by disease sub-type and include both gene fusion events and epigenetic regulatory mechanisms.
An international team of scientists, led by Lukas Chavez, PhD, of UC, San Diego, used genome-wide Hi-C to help identify novel intra- and inter-chromosomal structural variants and several genes, including RCOR2, ITGA6, LAMC1, and ARL4C. They concluded that these tumor-dependency genes and pathways play a central role in the oncogenic mechanisms of ependymoma and offer potential novel therapeutic targets. Learn more about this research:
Hear from Lukas Chaves in his talk entitled Unraveling Complex Structural Variants and ecDNA in Childhood Brain Tumors.
Gliomas
Pediatric high-grade gliomas, including glioblastoma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), cause brain tumors with low survival rates – the median survival range being from only 8-11 months for DIPG.
Learn how 3D genomics can add diagnostic value by identifying novel molecular drivers and potential therapeutic targets in tumors with no previously detectable drivers. Hear Dr. Matija Snuderl describe a pediatric patient with Stage 2 glioma who was initially treated with a subtotal resection of the tumor, but six months post-surgery experienced rapid progression. Comprehensive DNA and RNA sequencing of the primary tumor was inconclusive, with no driver mutations identified. A subsequent analysis using 3D genomics revealed a novel PD-L1 translocation, and immunohistochemical staining showed strong and diffuse PD-L1 expression.
Scientists from Northwestern University explored the effects of mutations in histone protein H3K27M on chromatin structure and transcriptional regulation. Their results identified tumor-specific enhancers and regulatory networks for known oncogenes, as well as structural variations that lead to potential enhancer hijacking and gene coamplification events. Ultimately, they demonstrated that 3D genome alterations might play a critical role in the epigenetic landscape and contribute to tumorigenesis in pediatric high-grade gliomas. Read more about this research
Leukemias
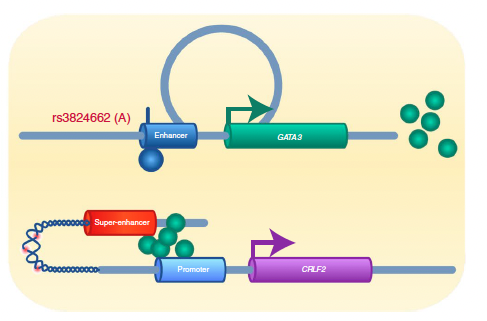
Yang et al., showed that GATA3 potentiates CRLF2–JAK–STAT signaling in hematopoietic cells (Nature Genetics 2022)
Acute lymphoblastic leukemias are the most common cancer in children and there is growing evidence of inherited susceptibility to this hematological malignancy. In a 2022 Nature Genetics paper, Yang et al, described how a germline noncoding variant contributes to oncogene activation, epigenetic regulation, and 3D genome reprogramming. Learn more about this research.
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a rare form of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. In a 2020 publication by Kloetgen et al, a team of scientists out of New York University detected widespread changes in 3D chromatin landscape in human T-ALL samples. Not only did they find that the 3D conformation of the MYC oncogene was altered between healthy and T-ALL patients, but that therapeutic intervention could restore the healthy 3D conformation. Learn more about this research.
Lineage-ambiguous leukemias are high-risk malignancies of poorly understood genetic basis. Monetfiorri et al demonstrated that structural variants or rearrangements of BCL11B gene result in enhancer hijacking of super-enhancers normally active in hematopoietic progenitor cells. Read our case study on this publication: HiChIP Reveals Enhancer Hijacking as an Oncogenic Driver of Ambiguous Leukemia
Ewing Sarcoma
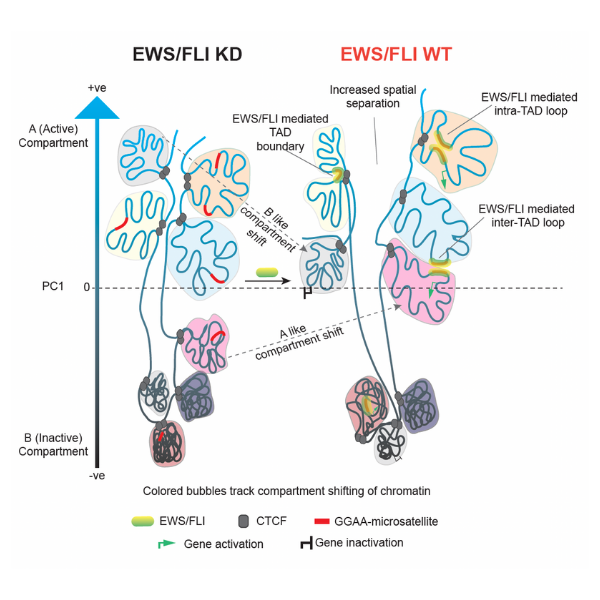
Model illustrating EWS/FLI chromatin changes that ultimately facilitates an oncogenic transcriptional state in Ewing sarcoma from Showpnil et al., in Nucleic Acids Research 2022
Ewing sarcoma is a highly aggressive pediatric cancer, causing bone tumors in children and adolescents. Genetically, Ewing sarcomas are characterized by chromosomal translocations between one gene and a transcription factor, resulting in dysregulation of thousands of downstream targets and oncogenesis. Research led by Stephen Lessnick and Emily Theisen at Nationwide Children’s Hospital used Arima Hi-C to precisely define the global changes in chromatin structure associated with Ewing sarcoma and further link these structural changes to alterations in gene expression. Specifically, they demonstrated the critical role of EWS/FLI in mediating genome-wide changes in chromatin configuration and that fusion transcription factors serve as master regulators through 3D reprogramming of chromatin. Learn more about this research.
Hemoglobinopathies
Mutations in the adult beta-globin gene can lead to various hemoglobinopathies, including sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia, which cause abnormal clotting, decreased red blood cell production, and anemia. However, studies have shown that the activation of gamma-globin — a subunit of fetal hemoglobin — can alleviate the symptoms of these diseases.
Xiaotian Zhang of the University of Michigan and colleagues used CRISPR-Cas9 to delete a portion of the 3′ end of the β-globin locus that includes a CTCF binding site and used Arima Hi-C technology to understand how this altered the 3D chromatin organization. They found that editing the gene-altered chromosomal loops in the beta-globin locus induced gamma-globin gene activation, suggesting genetic editing of this binding site can have therapeutic implications for treating hemoglobinopathies. Learn more about this research:
Hear from Xiaotian Zhang in his presentation entitled Paving the Way for 3D Genome Engineering and Therapy in Hemoglobinopathies.
How to Support the Rare Disease Community
There are many ways to support those living with rare diseases, their caregivers, and research into the causes and potential treatments.
- Participate in Rare Disease Day activities every February 28 and show your support on your favorite social channels using #RareDiseaseDay and @rarediseaseday
- Share your story about rare diseases and their impact on peoples’ lives to help raise awareness
- Support the rare disease research being undertaken at universities and children’s hospitals worldwide
If you are interested in using Arima technology to study a rare disease, please connect with us.




